Earned Value Management Example
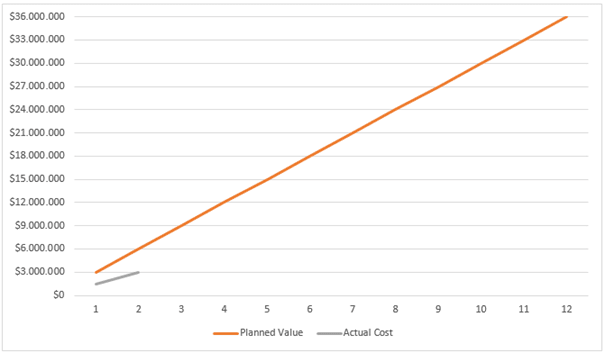
Let’s assume a 12-month railway project that is planned to spend $3M per month for a total budget at completion (BAC) of $36M. The project is 2 months along and according to the planned vs. actual cost figures is underspent by 50%.
We could assume therefore that the project is going well because it’s costing less than planned.
But after 2 months of work, 10 % of work has been completed so “EV” is 10% of the total $36M budget, which is $3.6M.
Budget at Completion (BAC) : $36M
Planned Value (PV) for 2 Months: $6M
EV: $3.6M
Actual Cost (AC): $3M
Schedule Variance (SV) : (Earned Value – Planned Value) = $3.6 – $6 = – $2.4 Behind the schedule
Cost Variance (CV): (Earned Value – Actual Cost) = $ 600K Under Budget
Cost Performance Index (CPI): (Earned Value / Actual Cost) = 1.2
Schedule Performance Index (SPI): (Earned value / Planned value) = 0.6
Estimate at Completion (EAC) : (Budget at Completion / Cost Performance Index) =$30M
Source: https://www.projectcubicle.com/earned-value-management-example/
Comments
Post a Comment